资料介绍
描述
自动驾驶汽车现在是最热门的话题。爱好者尝试使用树莓派和计算机视觉威廉希尔官方网站 制作它们。这是一种方法。制造自动驾驶汽车的另一种更简单的方法是线路跟随器、路径跟随器、迷宫求解机器人。这种机器人遵循在特定环境的地板上绘制的特定颜色线。我们可以使用相机或红外传感器制作它们。如果我说我不想在地板上画任何线,我希望它在隐形线上运行。这实际上是我在这里所做的。这个虚拟迷宫解算器/路径跟随机器人遵循来自远程 PC 的路径。所以机器人没有任何传感器,它只是从 PC 获取坐标——另一个软件机器人试图解决难题——硬件机器人/汽车的移动方式与软件机器人汽车的移动方式相同。现在让我分享一下我是如何做到这一点的。
部分:
硬件 -
电子产品 -
- 电机 - 4x
- 车轮(与电机兼容) - 4x
- HC05 蓝牙模块(发送/接收数据) - 1x
- 我制作的多功能机器人PCB(点此查看)- 1x
- 一些公母头针
- 焊线(在PCB上焊接东西)
使身体 -
- PVC 板(您可以使用任何板甚至纸张,我喜欢使用它们)
- 热胶和胶枪
软件 -
- Arduino.ide
- Python3(别担心,我会指导如何安装)
而已。现在让我们看看一切将如何运作。
原则(一切如何运作)
很简单,机器人将是一辆蓝牙控制的机器人汽车。python代码将在计算机上加载地图/迷宫并尝试解决它。硬件机器人将使用蓝牙从 Python 程序中获取数据并相应地移动。
python程序将通过比较颜色值来查找路径。我们的地图将包含白色路径。只要有一个白色像素,软件汽车就会前进,硬件机器人也会前进。现在让我们来吧。
制作机器人底盘
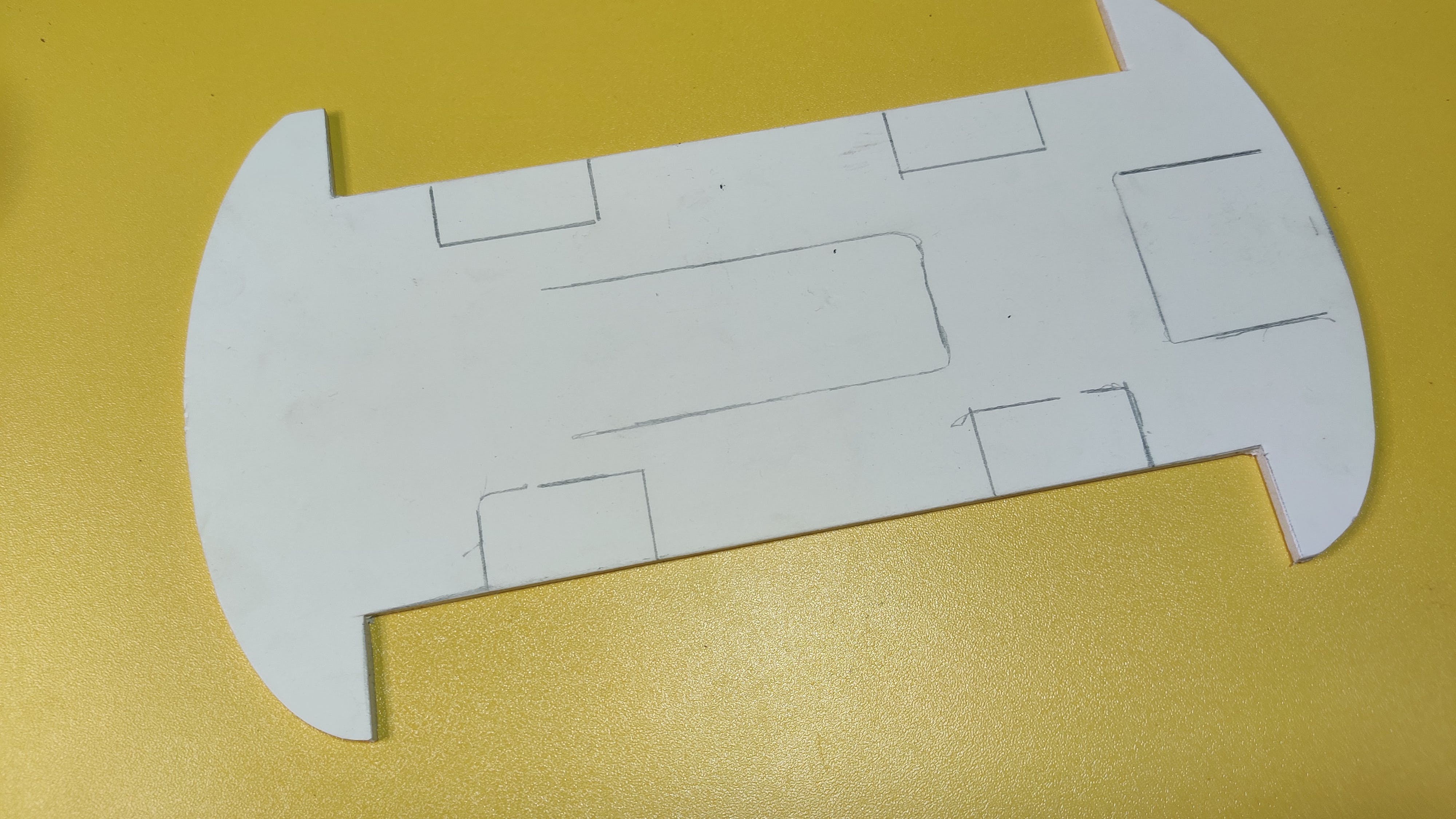
我拿了两张PVC片材,根据我的需要剪下来。你想怎么做是你的选择。切割板/床单后,我放置电机,用适当的电线连接它们。同一侧的两个电机作为一个电机,因此它们连接在一起。在图 6 中,我使用了一些母对母跳线将电机控制引脚连接到 PCB。之后,我添加了两个蓝色 PVC 件来装饰车身并连接轮子。
电路图和PCB
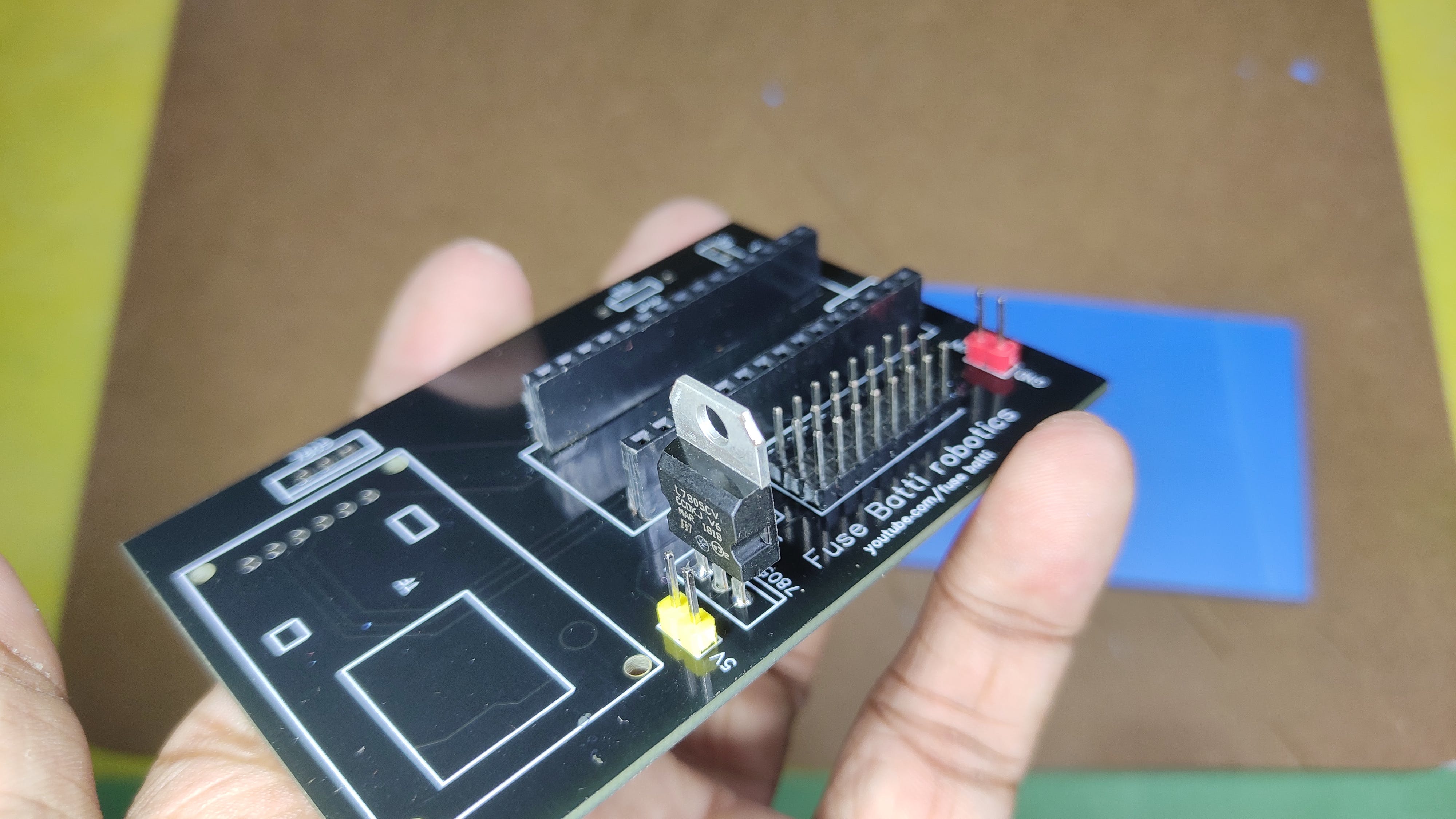
我使用EasyEDA 设计了电路。这很简单,我留下了除了 A4、A5(用于 I2C 通信)之外的所有interwetten与威廉的赔率体系 引脚,并添加了 SD 卡读卡器、蓝牙模块和 Arduino nano 的位置。蓝牙模块由跳线隔开(上传数据时,我们需要断开它)。我们不需要电阻,因为 Arduino 只会接收数据,不会写入。
之后,我从PCBWay.com 打印了 PCB。我发现他们的服务非常令人印象深刻。由于他们以更少的钱提供优质产品,我更喜欢将他们的服务用于我的 PCB。我去了pcb快速订购并上传了gerber文件。一切都是由网站自动完成的。在他们的工程师检查了我的 PCB 后,我在 3 天内付款并将它们从中国运到孟加拉国。质量令人惊叹,阻焊层,线条,玻璃般的外观一如既往地让我感到惊讶。
从这里获取 PCB 。
连接:
我连接了
- 左电机至 D5、D6
- 右电机至 D3、D4
蓝牙模块连接在专用端口上,但要准确
- VCC 至 5v
- 接地到接地
- 发送到 Arduino Rx
- Rx 到 Arduino Tx
你发什么,我收什么。所以Arduino的接收引脚(Rx)连接到蓝牙模块发送引脚(Tx)。
之后,从电机驱动模块为 PCB 供电。我总是喜欢在我的机器人项目中使用 7.4V 电源。两个锂电池就可以完成这项工作。3.7+3.7=7.4V,非常适合此类项目。
所以现在我们的蓝牙机器人已经准备好了。下一步是对其进行编程。
编程1:Arduino代码
现在是时候将程序上传到机器人了。由于蓝牙模块连接在硬件串行上,我在上传代码之前拔下了跳线。
首先,我定义了电机连接的引脚 -
// Declare motor pins
// motors of same side work as one
// so we can consider both as one.
int rightMotor1 = 2; // right side
int rightMotor2 = 3;
int leftMotor1 = 5; // left side
int leftMotor2 = 6;
然后我在 setup() 函数中将电机引脚声明为输出 -
// Set pin modes
pinMode(rightMotor1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(rightMotor2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(leftMotor1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(leftMotor2, OUTPUT);
然后我初始化串行通信以从蓝牙模块接收数据 -
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600);
它检查蓝牙模块所连接的串行端口的字节数据。
// Variable to store received data
byte command;
// Get command data from bluetooth serial port
command = Serial.read();
如果它收到 -
- 'f' 前进
- 'b' 向后
- l' 代表左和
- 'r' 表示正确的动作
每个电机都有两个引脚。如果我们需要将它们运行到一个方向,我们需要将一个引脚设为高电平,另一个引脚设为低电平。如果它们同时为高或低,电机将不会旋转。请参阅此示例以将汽车向前移动 -
if (command == 'f'){
// indicates forward motion
digitalWrite(rightMotor1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(rightMotor2, LOW);
digitalWrite(leftMotor1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(leftMotor2, LOW);}
通过这种组合,我们可以使机器人工作。
从 github 下载代码或从下面复制。我更喜欢下载以避免错误。
/* ** Virtual Path Following Robot *
* Robot Actuator's program
*
* This robot takes commands from a python program
* and follows those commands. This robot demonstrates
* virtual path following robots and it's scopes.
*
* *********** License: GPL3+ *************
* You should receive a copy of the license
* with this program.
*
* (c) author: ashraf minhaj
* mail : ashraf_minhaj@yahoo.com
*
* Tutorial for this project:
* http://youtube.com/fusebatti
* http://ashrafminhajfb.blogspot.com
*
* written on 15th Feb 2021
*/
// Declare motor pins
// motors of same side work as one
// so we can consider both as one.
int rightMotor1 = 2; // right side
int rightMotor2 = 3;
int leftMotor1 = 5; // left side
int leftMotor2 = 6;
// Variable to store received data
byte command;
void setup() {
// Set pin modes
pinMode(rightMotor1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(rightMotor2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(leftMotor1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(leftMotor2, OUTPUT);
// Initialize serial communication
// at 9600 buad rate
// sender/python code will also use
// the same buad
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Get command data from bluetooth serial port
command = Serial.read();
// Decide which way to go based on received data
if (command == 'f'){
// indicates forward motion
digitalWrite(rightMotor1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(rightMotor2, LOW);
digitalWrite(leftMotor1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(leftMotor2, LOW);
}
if (command == 'b'){
// Backward motion
digitalWrite(rightMotor1, LOW);
digitalWrite(rightMotor2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(leftMotor1, LOW);
digitalWrite(leftMotor2, HIGH);
}
if (command == 'r'){
// Right turn
digitalWrite(rightMotor1, LOW);
digitalWrite(rightMotor2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(leftMotor1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(leftMotor2, LOW);
}
if (command == 'l'){
// Left turn
digitalWrite(rightMotor1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(rightMotor2, LOW);
digitalWrite(leftMotor1, LOW);
digitalWrite(leftMotor2, HIGH);
}
if (command == 's'){
// Stops the robot/car
digitalWrite(rightMotor1, LOW);
digitalWrite(rightMotor2, LOW);
digitalWrite(leftMotor1, LOW);
digitalWrite(leftMotor2, LOW);
}
}
现在使用 Arduino.ide 上传代码并继续下一步。
Programmin2:Python 代码
我想你的电脑上安装了 python。如果没有,请转到并安装最新的稳定版 python。我使用 Python3.7.1,因为我发现它最稳定。在下载下载可执行安装程序时,双击它进行安装,然后单击“将python添加到环境变量路径”框,否则您将陷入灾难。
无论如何,现在让我们谈谈python程序。
我需要这个程序的两个库,pygame 和 pySerial。我像这样从命令提示符安装它们 -
$ pip install pygame
$ pip install pySerial
您在顶部看到的两个图像是迷宫和软件汽车。python程序读取它们-
bg = pygame.image.load("track1.png")
car = pygame.image.load("car.png")
要将数据从 PC 发送到 Arduino 蓝牙,我首先将蓝牙模块连接到我的 PC。步骤是 -
- 打开蓝牙
- 转到控制面板>设备管理器
- 搜索新设备
- 使用密码添加设备 (HC05) [默认密码为“0000”或“1234”]
而已。然后单击设备属性以获取端口号。在 HC05 中,在 py PC 中它位于“COM8”中。所以python像这样连接 -
PORT = "COM8"
BUADRATE = 9600
robot = serial.Serial(PORT, BUADRATE) # connect robot
为了让机器人先检查周围环境,我找到了汽车的中心,然后检查了周围环境——
# find the center of the car and draw a point on that
center_x, center_y = (int(car_x + 40 /2), int(car_y + 40 / 2))
代码的其余部分是检查周围环境并转动或移动汽车。如果它向前或任何方向,它会通过这样的串行端口(字节数据)将该数据发送到 Arduino -
# start the robot
robot.write(b'f')
# turn left
robot.write(b'l')
现在从 github 下载完整代码或从下面复制 -
"""
** Virtual Path Follower Robot **
License: GPL3
You should receive a copy of license with this program.
(c) author: ashraf minhaj
mail : ashraf_minhaj@yahoo.com
Written on 15th Feb 2021
"""
""" install -
$ pip install pygame
$ pip install pySerial
"""
# import library
import pygame
import serial
from time import sleep
# robot port and buadrate
# change these according to your need
PORT = "COM8"
BUADRATE = 9600
# initialize things
pygame.init()
robot = serial.Serial(PORT, BUADRATE) # connect robot
# create window with size (our image size)
window = pygame.display.set_mode((700,400)) # track 1
#window = pygame.display.set_mode((1155,399)) # track 2
# load image file
bg = pygame.image.load("track1.png")
#bg = pygame.image.load("track2.png")
car = pygame.image.load("car.png")
car = pygame.transform.scale(car, (40, 40)) # resize car image
""" main loop varibales and things """
# set up timer clock
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
# initial x y axis position of the car
car_x = 30
car_y = 260
JUMP_VALUE = 25 # turning point value
direction = 'y_up' # cars current direction
run = 1
# start the robot
robot.write(b'f')
DELAY = .400
# main loop
while run:
clock.tick(30) # update the window/run loop by this speed
#check for events
for event in pygame.event.get():
# quit button clicked
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
run = 0
# position images
window.blit(bg, (0, 0)) # load the track image
window.blit(car, (car_x, car_y)) # the car image
# record last x, y pos of car
last_x, last_y = car_x, car_y
# find the center of the car and draw a point on that
center_x, center_y = (int(car_x + 40 /2), int(car_y + 40 / 2))
pygame.draw.circle(window, (0,255,255), (center_x, center_y), 5, 5)
# check surrounding (4 direction data)
# the calibration value is the pixel from car's sensor/mid point
# so it checks for road info 30 pixels far from the sensor.
# 255 means we have a clear white road
cal_value = 30 # calibrate this to get good data
y_up = window.get_at((center_x, center_y - cal_value))[0]
y_down = window.get_at((center_x, center_y + cal_value))[0]
x_right = window.get_at((center_x + cal_value, center_y))[0]
x_left = window.get_at((center_x - cal_value, center_y))[0]
#print("y_up ", y_up)
#print("y_down ", y_down)
#print("x_right", x_right)
#print("x_left ", x_left)
#print("-----------")
# determine which way to go
# go up
if y_up == 255 and direction == 'y_up' and x_left != 255 and x_right != 255:
# move up
car_y -= 2 # decrease pixel and move the car on y axis
# make the turn
if y_up == 255 and direction == 'y_up' and x_left != 255 and x_right == 255:
# make a right turn
direction = 'x_right'
car_y -= JUMP_VALUE
car_x += JUMP_VALUE
car = pygame.transform.rotate(car, -90)
window.blit(car, (car_x, car_y))
print('Turn Right')
robot.write(b'r')
sleep(DELAY)
robot.write(b'f')
# go x right
if y_up != 255 and direction == 'x_right' and y_down != 255 and x_right == 255:
car_x += 2
if y_down == 255 and direction == 'x_right' and x_left == 255 and x_right == 255:
# make a turn from x_right
car = pygame.transform.rotate(car, -90)
direction = 'y_down'
car_y += JUMP_VALUE + 5
car_x += JUMP_VALUE
window.blit(car, (car_x, car_y))
print('Turn Right')
robot.write(b'r')
sleep(DELAY)
robot.write(b'f')
# go y down
if y_down == 255 and direction == 'y_down' and x_left != 255 and x_right != 255:
# move down
car_y += 2
# left turn
if y_down == 255 and direction == 'y_down' and x_left != 255 and x_right == 255:
# turn from y_down
car = pygame.transform.rotate(car, 90)
direction = 'x_right'
car_y += JUMP_VALUE
car_x += JUMP_VALUE
print('Turn left')
robot.write(b'l')
sleep(DELAY)
robot.write(b'f')
# turn to y up
if y_up == 255 and direction == 'x_right' and x_left == 255 and x_right == 255:
# turn from y_down
car = pygame.transform.rotate(car, 90)
direction = 'y_up'
car_y -= JUMP_VALUE + 5
car_x += JUMP_VALUE
print('Turn left')
robot.write(b'l')
sleep(DELAY)
robot.write(b'f')
# if car is stopped
if car_x == last_x and car_y == last_y:
# stop the engine sound
print("STOPPED")
robot.write(b's')
pygame.display.update() # update the window
pygame.quit() #close everything
通电,我们走吧
我使用两节 18650 电池为机器人供电。然后运行 Python 程序。它的表现如何?你可以在视频中看到。
这个机器人最好的部分是你不需要不时更改机器人的代码。您只需要相应地更改 python 程序。而已。
未来范围:
该机器人可用于带有一些板载传感器的行业,以确定错误或滑出路径并避开障碍物。天空是极限,你的大脑是主人。
谢谢你。
- AI解迷宫机器人
- 检测机器人开源分享
- 坦克机器人开源分享
- 扫地机器人开源资料 43次下载
- 机器人守卫开源分享
- 伺服机器人开源分享
- 英雄机器人开源
- 机器人开源案例
- 赫伯特机器人虚拟宠物开源分享
- 基于DSP和PC的农业机器人控制系统 17次下载
- 竞赛机器人制作威廉希尔官方网站 PDF电子书免费下载 44次下载
- 面向ABB IRB4600机器人的虚拟示教系统研究 2次下载
- 基于LPC1114的迷宫机器人的设计与实现 13次下载
- 基于ARM的机器人走迷宫控制系统与算法设计 27次下载
- 基于虚拟监控威廉希尔官方网站 的机器人系统 10次下载
- 字节发布机器人领域首个开源视觉-语言操作大模型,激发开源VLMs更大潜能 360次阅读
- 机器人威廉希尔官方网站 中常用的路径规划算法的开源库 842次阅读
- 工业机器人虚拟仿真软件简述 5548次阅读
- 面对疫情 医疗机器人能帮上什么忙? 2126次阅读
- dfrobotSparki机器人套装简介 2064次阅读
- 工业机器人编程入门_工业机器人的编程要求 9571次阅读
- 医用机器人的定义_医用机器人发展 3122次阅读
- 医用机器人的功能_医用机器人分类 2227次阅读
- 协作机器人的起源_为什么需要协作机器人 8127次阅读
- 如何区分机器人、协作机器人和移动机器人? 6828次阅读
- 软体机器人 前所未见的机器人 3692次阅读
- 机器人的最佳编程语言是什么?机器人十大流行编程语言汇总 3.4w次阅读
- 工业机器人虚拟仿真软件是一个很好的工业机器人入门途径 3.4w次阅读
- 机器人系统常用仿真软件介绍和效果 8375次阅读
- 工业机器人虚拟样机系统的研究 1385次阅读
下载排行
本周
- 1SMD LED选型手册 贴片灯珠
- 5.47 MB | 4次下载 | 免费
- 2明纬S-50-24开关电源电路图.pdf
- 0.10 MB | 2次下载 | 5 积分
- 3基本半导体产品在Sic逆变焊机中的应用
- 7.27 MB | 2次下载 | 免费
- 4加密芯片的一种破解方法和对应加密方案改进设计
- 0.29 MB | 1次下载 | 免费
- 5多功能MPU芯片GC9005数据手册
- 2.67 MB | 1次下载 | 免费
- 6基本半导体产品在125kW工商业储能PCS中的应用
- 10.74 MB | 1次下载 | 免费
- 7MOSFET参数解读
- 1.59 MB | 1次下载 | 2 积分
- 8550W充电机原理图
- 0.13 MB | 1次下载 | 6 积分
本月
- 1使用单片机实现七人表决器的程序和仿真资料免费下载
- 2.96 MB | 44次下载 | 免费
- 2美的电磁炉维修手册大全
- 1.56 MB | 16次下载 | 5 积分
- 33314A函数发生器维修手册
- 16.30 MB | 13次下载 | 免费
- 4STM32F101x8/STM32F101xB手册
- 1.69 MB | 8次下载 | 1 积分
- 5感应笔电路图
- 0.06 MB | 8次下载 | 免费
- 6使用TL431设计电源
- 0.67 MB | 7次下载 | 免费
- 7不对称半桥(AHB)反激变换器的分析与设计
- 0.68 MB | 6次下载 | 1 积分
- 8LZC3106G高性能谐振控制器中文手册
- 1.29 MB | 5次下载 | 1 积分
总榜
- 1matlab软件下载入口
- 未知 | 935119次下载 | 10 积分
- 2开源硬件-PMP21529.1-4 开关降压/升压双向直流/直流转换器 PCB layout 设计
- 1.48MB | 420062次下载 | 10 积分
- 3Altium DXP2002下载入口
- 未知 | 233084次下载 | 10 积分
- 4电路仿真软件multisim 10.0免费下载
- 340992 | 191367次下载 | 10 积分
- 5十天学会AVR单片机与C语言视频教程 下载
- 158M | 183335次下载 | 10 积分
- 6labview8.5下载
- 未知 | 81581次下载 | 10 积分
- 7Keil工具MDK-Arm免费下载
- 0.02 MB | 73807次下载 | 10 积分
- 8LabVIEW 8.6下载
- 未知 | 65987次下载 | 10 积分
 电子发烧友App
电子发烧友App
















 创作
创作 发文章
发文章 发帖
发帖  提问
提问  发资料
发资料 发视频
发视频









评论