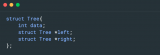
最近总结了一些数据结构和算法相关的题目,这是第一篇文章,关于二叉树的。先上二叉树的数据结构:
class TreeNode{ int val; //左孩子 TreeNode left; //右孩子 TreeNode right;}
二叉树的题目普遍可以用递归和迭代的方式来解
1. 求二叉树的最大深度
int maxDeath(TreeNode node){ if(node==null){ return 0; } int left = maxDeath(node.left); int right = maxDeath(node.right); return Math.max(left,right) + 1;}
2. 求二叉树的最小深度
int getMinDepth(TreeNode root){ if(root == null){ return 0; } return getMin(root); } int getMin(TreeNode root){ if(root == null){ return Integer.MAX_VALUE; } if(root.left == null&&root.right == null){ return 1; } return Math.min(getMin(root.left),getMin(root.right)) + 1; }
3. 求二叉树中节点的个数
int numOfTreeNode(TreeNode root){ if(root == null){ return 0; } int left = numOfTreeNode(root.left); int right = numOfTreeNode(root.right); return left + right + 1; }
4. 求二叉树中叶子节点的个数
int numsOfNoChildNode(TreeNode root){ if(root == null){ return 0; } if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){ return 1; } return numsOfNodeTreeNode(root.left)+numsOfNodeTreeNode(root.right); }
5. 求二叉树中第k层节点的个数
int numsOfkLevelTreeNode(TreeNode root,int k){ if(root == null||k<1){ return 0; } if(k==1){ return 1; } int numsLeft = numsOfkLevelTreeNode(root.left,k-1); int numsRight = numsOfkLevelTreeNode(root.right,k-1); return numsLeft + numsRight; }
6. 判断二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
boolean isBalanced(TreeNode node){ return maxDeath2(node)!=-1; } int maxDeath2(TreeNode node){ if(node == null){ return 0; } int left = maxDeath2(node.left); int right = maxDeath2(node.right); if(left==-1||right==-1||Math.abs(left-right)>1){ return -1; } return Math.max(left, right) + 1; }
7.判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
什么是完全二叉树呢?参见
boolean isCompleteTreeNode(TreeNode root){ if(root == null){ return false; } Queue
8. 两个二叉树是否完全相同
boolean isSameTreeNode(TreeNode t1,TreeNode t2){ if(t1==null&&t2==null){ return true; } else if(t1==null||t2==null){ return false; } if(t1.val != t2.val){ return false; } boolean left = isSameTreeNode(t1.left,t2.left); boolean right = isSameTreeNode(t1.right,t2.right); return left&&right; }
9. 两个二叉树是否互为镜像
boolean isMirror(TreeNode t1,TreeNode t2){ if(t1==null&&t2==null){ return true; } if(t1==null||t2==null){ return false; } if(t1.val != t2.val){ return false; } return isMirror(t1.left,t2.right)&&isMirror(t1.right,t2.left); }
10. 翻转二叉树or镜像二叉树
TreeNode mirrorTreeNode(TreeNode root){ if(root == null){ return null; } TreeNode left = mirrorTreeNode(root.left); TreeNode right = mirrorTreeNode(root.right); root.left = right; root.right = left; return root; }
11. 求两个二叉树的最低公共祖先节点
TreeNode getLastCommonParent(TreeNode root,TreeNode t1,TreeNode t2){ if(findNode(root.left,t1)){ if(findNode(root.right,t2)){ return root; }else{ return getLastCommonParent(root.left,t1,t2); } }else{ if(findNode(root.left,t2)){ return root; }else{ return getLastCommonParent(root.right,t1,t2) } } } // 查找节点node是否在当前 二叉树中 boolean findNode(TreeNode root,TreeNode node){ if(root == null || node == null){ return false; } if(root == node){ return true; } boolean found = findNode(root.left,node); if(!found){ found = findNode(root.right,node); } return found; }
12. 二叉树的前序遍历
迭代解法
ArrayList
递归解法
ArrayList
13. 二叉树的中序遍历
ArrayList
14.二叉树的后序遍历
ArrayList
15.前序遍历和后序遍历构造二叉树
TreeNode buildTreeNode(int[] preorder,int[] inorder){ if(preorder.length!=inorder.length){ return null; } return myBuildTree(inorder,0,inorder.length-1,preorder,0,preorder.length-1); } TreeNode myBuildTree(int[] inorder,int instart,int inend,int[] preorder,int prestart,int preend){ if(instart>inend){ return null; } TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[prestart]); int position = findPosition(inorder,instart,inend,preorder[start]); root.left = myBuildTree(inorder,instart,position-1,preorder,prestart+1,prestart+position-instart); root.right = myBuildTree(inorder,position+1,inend,preorder,position-inend+preend+1,preend); return root; } int findPosition(int[] arr,int start,int end,int key){ int i; for(i = start;i<=end;i++){ if(arr[i] == key){ return i; } } return -1; }
16.在二叉树中插入节点
TreeNode insertNode(TreeNode root,TreeNode node){ if(root == node){ return node; } TreeNode tmp = new TreeNode(); tmp = root; TreeNode last = null; while(tmp!=null){ last = tmp; if(tmp.val>node.val){ tmp = tmp.left; }else{ tmp = tmp.right; } } if(last!=null){ if(last.val>node.val){ last.left = node; }else{ last.right = node; } } return root; }
17.输入一个二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中节点值的和等于输入整数所有的路径
void findPath(TreeNode r,int i){ if(root == null){ return; } Stack
18.二叉树的搜索区间
给定两个值 k1 和 k2(k1 < k2)和一个二叉查找树的根节点。找到树中所有值在 k1 到 k2 范围内的节点。即打印所有x (k1 <= x <= k2) 其中 x 是二叉查找树的中的节点值。返回所有升序的节点值。
ArrayList
19.二叉树的层次遍历
ArrayList
20.二叉树内两个节点的最长距离
二叉树中两个节点的最长距离可能有三种情况:1.左子树的最大深度+右子树的最大深度为二叉树的最长距离2.左子树中的最长距离即为二叉树的最长距离3.右子树种的最长距离即为二叉树的最长距离因此,递归求解即可
private static class Result{ int maxDistance; int maxDepth; public Result() { } public Result(int maxDistance, int maxDepth) { this.maxDistance = maxDistance; this.maxDepth = maxDepth; } } int getMaxDistance(TreeNode root){ return getMaxDistanceResult(root).maxDistance; } Result getMaxDistanceResult(TreeNode root){ if(root == null){ Result empty = new Result(0,-1); return empty; } Result lmd = getMaxDistanceResult(root.left); Result rmd = getMaxDistanceResult(root.right); Result result = new Result(); result.maxDepth = Math.max(lmd.maxDepth,rmd.maxDepth) + 1; result.maxDistance = Math.max(lmd.maxDepth + rmd.maxDepth,Math.max(lmd.maxDistance,rmd.maxDistance)); return result; }
21.不同的二叉树
给出 n,问由 1…n 为节点组成的不同的二叉查找树有多少种?
int numTrees(int n ){ int[] counts = new int[n+2]; counts[0] = 1; counts[1] = 1; for(int i = 2;i<=n;i++){ for(int j = 0;j
22.判断二叉树是否是合法的二叉查找树(BST)
一棵BST定义为:节点的左子树中的值要严格小于该节点的值。节点的右子树中的值要严格大于该节点的值。左右子树也必须是二叉查找树。一个节点的树也是二叉查找树。
public int lastVal = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public boolean firstNode = true; public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { // write your code here if(root==null){ return true; } if(!isValidBST(root.left)){ return false; } if(!firstNode&&lastVal >= root.val){ return false; } firstNode = false; lastVal = root.val; if (!isValidBST(root.right)) { return false; } return true; }
深刻的理解这些题的解法思路,在面试中的二叉树题目就应该没有什么问题
-
二叉树
+关注
关注
0文章
74浏览量
12324
原文标题:一篇文章搞定面试中的二叉树
文章出处:【微信号:TheAlgorithm,微信公众号:算法与数据结构】欢迎添加关注!文章转载请注明出处。
发布评论请先 登录
相关推荐
二叉查找树(GIF动图讲解)
二叉树算法在单总线威廉希尔官方网站 中的应用
二叉树层次遍历算法的验证
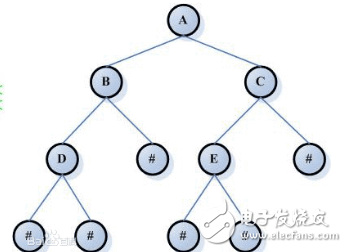




 关于二叉树一些数据结构和算法相关的题目
关于二叉树一些数据结构和算法相关的题目










评论