1.算术生成算法--求和accumulate
算术生成算法头文件< numeric >
算法简介:
容器区间元素求和:accumulate
像容器中添加元素:fill
accumulate求和:
accumulate(const _InIt _First, const _InIt _Last, _Ty _Val)
形参:_First、_Last --元素区间
_Val --累加的起始值
重载版本:
accumulate(const _InIt _First, const _InIt _Last, _Ty _Val, _Fn _Reduce_op)
形参:_First、_Last --元素区间
_Val --起始值
_Reduce_op --运算规则(加、减、乘、除。。。)
#include < vector >
#include < iostream >
#include < numeric >
#include < functional >
using namespace std;
void test()
{
vector< int >vtr;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
{
vtr.push_back(i);
}
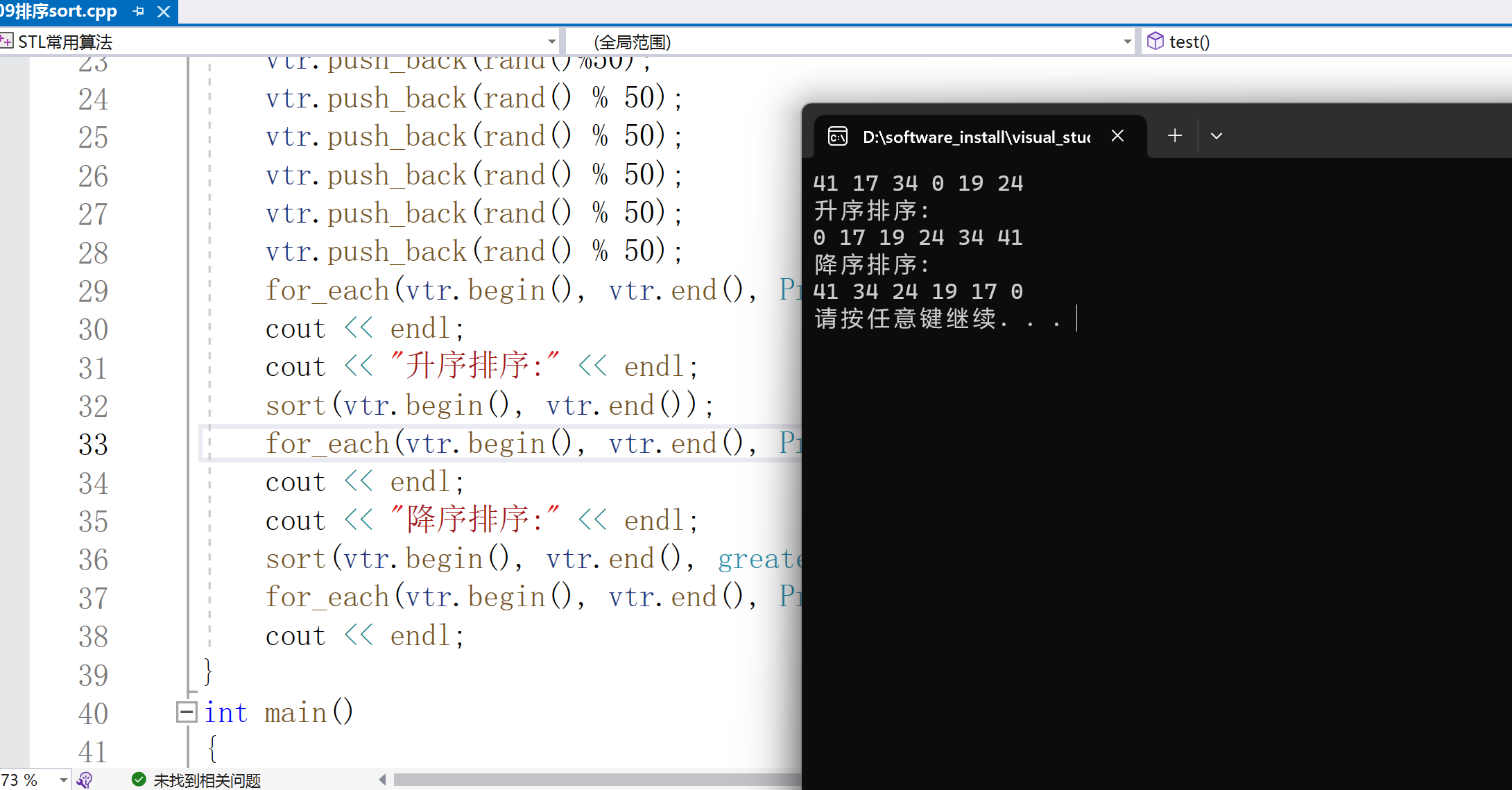
auto sum=accumulate(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), 0);
cout < < "sum=" < < sum < < endl;
sum=accumulate(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), 1, multiplies< int >());
cout < < "sum=" < < sum < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
2.算术生成算法--填充fill
void fill(const _FwdIt _First, const _FwdIt _Last, const _Ty& _Val)
函数功能:容器填充
形参:_First、_Last --要填充的区间
_Val --要填充的值
#include < iostream >
#include < vector >
#include < numeric >
#include < algorithm >
using namespace std;
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
};
void test()
{
vector< int >vtr;
vtr.resize(10);
fill(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), 666);
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.常用集合算法--求交集set_intersection
常用集合算法:--头文件< algorithm >
求交集(即两个容器相同元素部分):set_intersection()
求并集:set_union()
求差集:set_different()
求交集:
_OutIt set_intersection(_InIt1 _First1, _InIt1 _Last1, _InIt2 _First2, _InIt2 _Last2, _OutIt _Dest, _Pr _Pred)
_OutIt set_intersection(_First1, _Last1, _First2, _Last2, _Dest);
形参:_First1、_Last1 --容器1的区间范围
_First2、_Last2 --容器2的区间范围
_Dest --结果保存起始迭代器
_Pred --排序规则
返回值:返回结果的最后一个元素的下一个位置的迭代器(end)
注意:求交集必须保证元素有序,默认是从小到大
#include < iostream >
#include < vector >
#include < algorithm >
using namespace std;
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
};
void test()
{
vector< int >t1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
vector< int >t2 = { 1,3,5,7,8,9 };
vector< int >t3;
//设置t3容器大小,min()为获取最小值
t3.resize(min(t1.size(), t2.size()));
vector< int >::iterator ret=set_intersection(t1.begin(), t1.end(), t2.begin(), t2.end(), t3.begin());
set_intersection()
cout < < "t1与t2的交集为:" < < endl;
for_each(t3.begin(), ret, Print());
cout < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
4.常用集合算法--求并集set_union
求并集:
set_union(_InIt1 _First1, _InIt1 _Last1, _InIt2 _First2, _InIt2 _Last2, _OutIt _Dest)
set_union(_ExPo&&, _FwdIt1 _First1, _FwdIt1 _Last1, _FwdIt2 _First2, _FwdIt2 _Last2, _FwdIt3 _Dest,_Pr _Pred)
形参:_First1、_Last1 --容器1的区间范围
_First2、_Last2 --容器2的区间范围
_Dest --结果保存起始迭代器
_Pred --排序规则
返回值:返回结果的最后一个元素的下一个位置的迭代器(end)
注意:求并集必须保证元素有序,默认是从小到大
#include < iostream >
#include < algorithm >
#include < vector >
using namespace std;
class print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
};
void test()
{
vector< int >v1 = { 1,3,4,6,8,9 };
vector< int >v2 = { 2,3,3,4,7,9,10 };
vector< int >v3;
v3.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
vector< int >::iterator ret=set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
cout < < "v1与v2的并集:" < < endl;
for_each(v3.begin(), ret, print());
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
5.常用集合算法--求差集set_difference
求差集:set_difference()
_OutIt set_difference(_InIt1 _First1, _InIt1 _Last1, _InIt2 _First2, _InIt2 _Last2, _OutIt _Dest)
_OutIt set_difference(_InIt1 _First1, _InIt1 _Last1, _InIt2 _First2, _InIt2 _Last2, _OutIt _Dest, _Pr _Pred)
形参:_First1、_Last1 --容器1的区间范围
_First2、_Last2 --容器2的区间范围
_Dest --结果保存起始迭代器
_Pred --排序规则
返回值:返回结果的最后一个元素的下一个位置的迭代器(end)
注意:求差集必须保证元素有序,默认是从小到大
#include < iostream >
#include < algorithm >
#include < vector >
using namespace std;
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
};
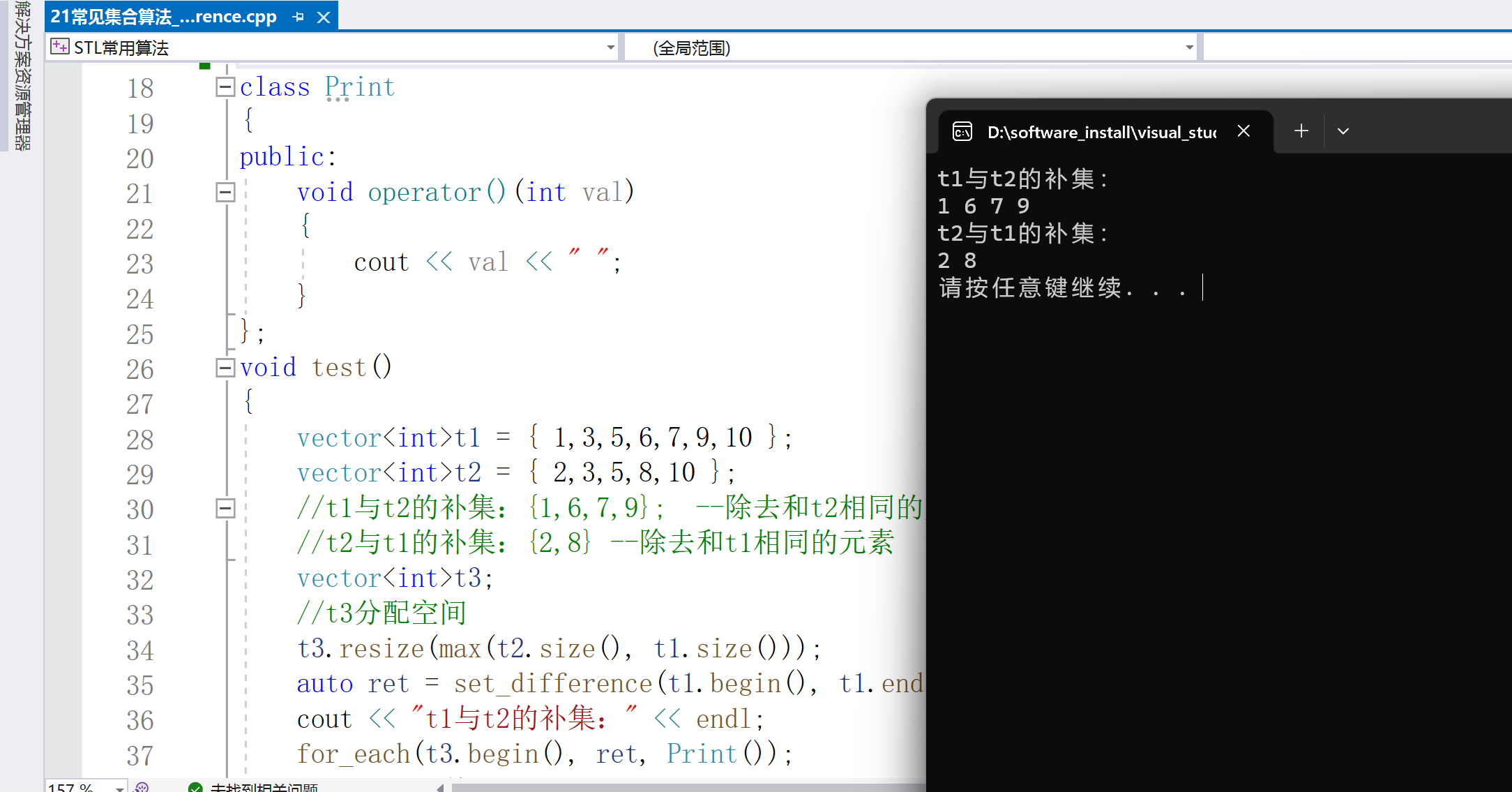
void test()
{
vector< int >t1 = { 1,3,5,6,7,9,10 };
vector< int >t2 = { 2,3,5,8,10 };
//t1与t2的补集:{1,6,7,9}; --除去和t2相同的元素
//t2与t1的补集:{2,8} --除去和t1相同的元素
vector< int >t3;
//t3分配空间
t3.resize(max(t2.size(), t1.size()));
auto ret = set_difference(t1.begin(), t1.end(), t2.begin(), t2.end(), t3.begin());
cout < < "t1与t2的补集:" < < endl;
for_each(t3.begin(), ret, Print());
cout < < endl;
ret = set_difference(t2.begin(), t2.end(), t1.begin(), t1.end(), t3.begin());
cout < < "t2与t1的补集:" < < endl;
for_each(t3.begin(), ret, Print());
cout < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
算法
+关注
关注
23文章
4606浏览量
92763 -
C++
+关注
关注
22文章
2106浏览量
73573 -
STL
+关注
关注
0文章
86浏览量
18313
发布评论请先 登录
相关推荐
c语言入门知识之STL篇
这周终于可以给大家把STL方面的面试题总结出来了,突然发现它里面的细节非常多,只有你想不到的,没有它没有的。对于C++程序员来说,STL库里面的知识也是非常重要的,只要想在威廉希尔官方网站
这条路线上有长远的发展,那么就一定要掌握它。不管是学
C++ STL的概念及举例
本篇文章是作者本人使用STL 后的一些看法, 对於想要靠此文章学习STL, 是不可能的. 建议叁后面介绍的一些书入门.
STL的概念
在STL 中, 大至上分
发表于 08-30 11:39
•1407次阅读
STL算法在GIS中的应用
使用STL 算法实现GIS 算法可以保证它的简洁和高效该文结合C++代码实例抽象出了地理算子的概念应用在GIS 算法当中通过定制适配器来消除
发表于 06-28 16:55
•33次下载
C++课程资料详细资料合集包括了:面向对象程序设计与C++,算法,函数等
本文档的主要内容详细介绍的是C++课程资料资料合集包括了:面向对象程序设计与C++,算法,函数,概述, C++语言基础,构造数据类型,数据类型,C+
发表于 07-09 08:00
•18次下载
C语言教程:STL-for-each算法
C语言教程:STL-for-each算法(电源威廉希尔官方网站
版面费5400)-文档为C语言教程:STL-for-each
发表于 09-17 12:42
•3次下载

C++ STL基本概念是什么
STL,英文全称 standard template library,中文可译为标准模板库或者泛型库,其包含有大量的模板类和模板函数,是 C++ 提供的一个基础模板的集合,用于完成诸如输入/输出、数学计算等功能。

C++入门之通用算法
C++ 是一种强大的编程语言,它提供了许多通用算法,可以用于各种容器类型。这些算法是通过迭代器来操作容器中的元素,因此它们是通用的,可以用于不同类型的容器。在本篇博客中,我们将详细介绍 C++




 c++之STL算法(三)
c++之STL算法(三)










评论